Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common cardiovascular condition that affects millions of people in India. This condition occurs when the arteries are narrowing, which can reduce the amount of oxygen-rich blood flow to the leg muscles and cause pain, fatigue, and other symptoms. If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications such as stroke, heart attack, or even amputation.
Therefore, it is important for patients to understand this condition to reduce their risk of developing long-term complications and seek medical care as soon as possible if they experience any signs or symptoms.
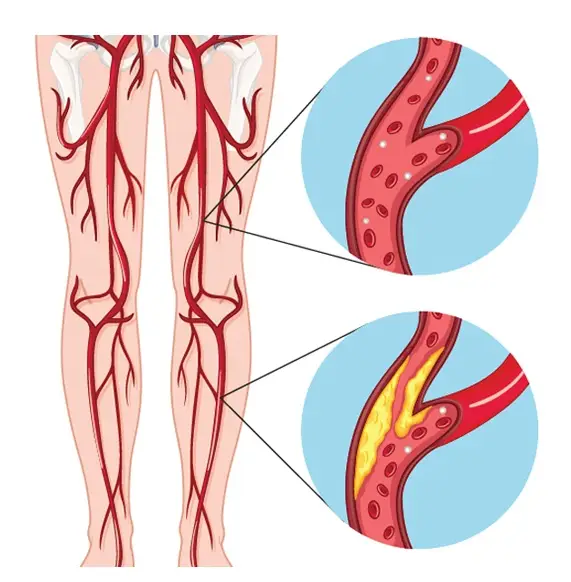
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is caused by narrowing arteries in the limbs, resulting in reduced oxygen-rich blood flow to muscles throughout the body. This decreased circulation causes insufficient oxygen and a lack of nutrients to be delivered to the tissues, leading to pain and, eventually, tissue damage.
PAD can also decrease physical performance due to an inadequate oxygen supply and fuel for muscle contraction. Additionally, plaque buildup in the arteries puts patients at increased risk for stroke or heart attack. Early detection and diagnosis are essential to prevent these long-term complications.
Symptoms
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common condition characterized by narrowed arteries in the limbs, resulting in reduced oxygen-rich blood flow to muscles in the legs or arms. The most common symptoms of PAD are leg pain, cramping, and weakness during physical activity. These symptoms can cause difficulty with everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or standing for long periods.
Additionally, patients may experience coldness in their lower legs and feet due to decreased circulation. It is important to note that these symptoms can worsen if not taken care of properly and on time. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential that you seek medical attention immediately so that your doctor can provide the appropriate treatment and help you manage your PAD effectively.
Causes
The primary cause of peripheral artery disease (PAD) is atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the legs and feet. This plaque can form due to a combination of lifestyle factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol, making it much more likely to occur.
These risk factors may include age (over age 50), obesity, physical inactivity, family history of stroke or heart disease, drinking large amounts of alcohol, and an unhealthy diet high in saturated fat. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as lupus and kidney failure, can increase an individual's risk of developing PAD. It is important to note that recognizing the potential warning signs of PAD is essential for prevention and early detection.
Diagnosis
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is typically diagnosed through physical exams of the legs and an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test, which compares the blood pressure readings in each arm and leg. Other imaging tests like ultrasound or angiography may also detect a narrowing of the arteries and blockages due to plaque buildup. These tests can help diagnose PAD earlier and provide important information for treatment decisions.
Any diagnosis of PAD must be accurate, as this can help guide treatment decisions to keep the condition from progressing and causing more serious long-term problems such as stroke or heart attack. By detecting PAD early on, patients can begin lifestyle changes or start taking medication that can slow or reverse artery damage, thus preventing these bad outcomes.
Treatment
Treatment for peripheral artery disease (PAD) can involve a combination of medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle changes. Medications used to treat PAD could include aspirin or other drugs to reduce cholesterol and blood thinners that help prevent clots from forming in the arteries. Surgical procedures such as angioplasty and stenting are also effective treatments, as they widen the arteries to allow more oxygen-rich blood flow to the legs and feet.
Lastly, lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly, avoiding smoking, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress levels can make a big difference in managing PAD symptoms.
It is important to note that successful outcomes vary based on individual health status and follow-through with treatment plans. However, many patients have been able to manage their PAD symptoms through these various treatments while still enjoying an active lifestyle.
Recovery
The recovery process for peripheral artery disease (PAD) can be long and difficult, but following doctor's orders and making lifestyle changes can help. Patients must attend follow-up appointments with their physicians to monitor their condition and ensure treatments work.
Medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms and prevent further complications, such as blood thinners from preventing clotting and cholesterol-lowering drugs from reducing plaque buildup. Additionally, regular exercise, healthy eating habits, and stress management are all important elements of PAD recovery.
It is also recommended that patients get adequate rest, wear comfortable shoes and socks and use heat or cold therapy to manage any pain or discomfort associated with the condition.
Prevention
There are several ways to help prevent peripheral artery disease (PAD) from developing or recurring.
Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, and exercising regularly can all help reduce the risk of PAD. Managing stress levels and controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol is also important.
In addition, avoiding activities that can cause blockages in the arteries, such as smoking, should be avoided, and medications prescribed by doctors should be taken as directed. Regular checkups with a healthcare professional can catch any signs of PAD early, allowing treatment and prevention measures to be taken.Conclusion
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a serious condition that can lead to serious complications, so it is important for those at risk or recognizing any symptoms of PAD to seek medical attention. In addition to the treatments a physician provides, lifestyle changes such as healthy eating and regular exercise can help with recovery from PAD. Taking steps such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress levels, and controlling risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol can also help prevent PAD from developing or recurring.


