Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, is an event in which the blood supply to the heart is blocked or reduced, resulting in tissue death and major damage to the heart. In India, it is estimated that one-third of all deaths are due to cardiovascular diseases such as MI. Therefore, those at risk of developing MI must understand the condition and take steps to manage and prevent its progression.
Myocardial infarction (MI)
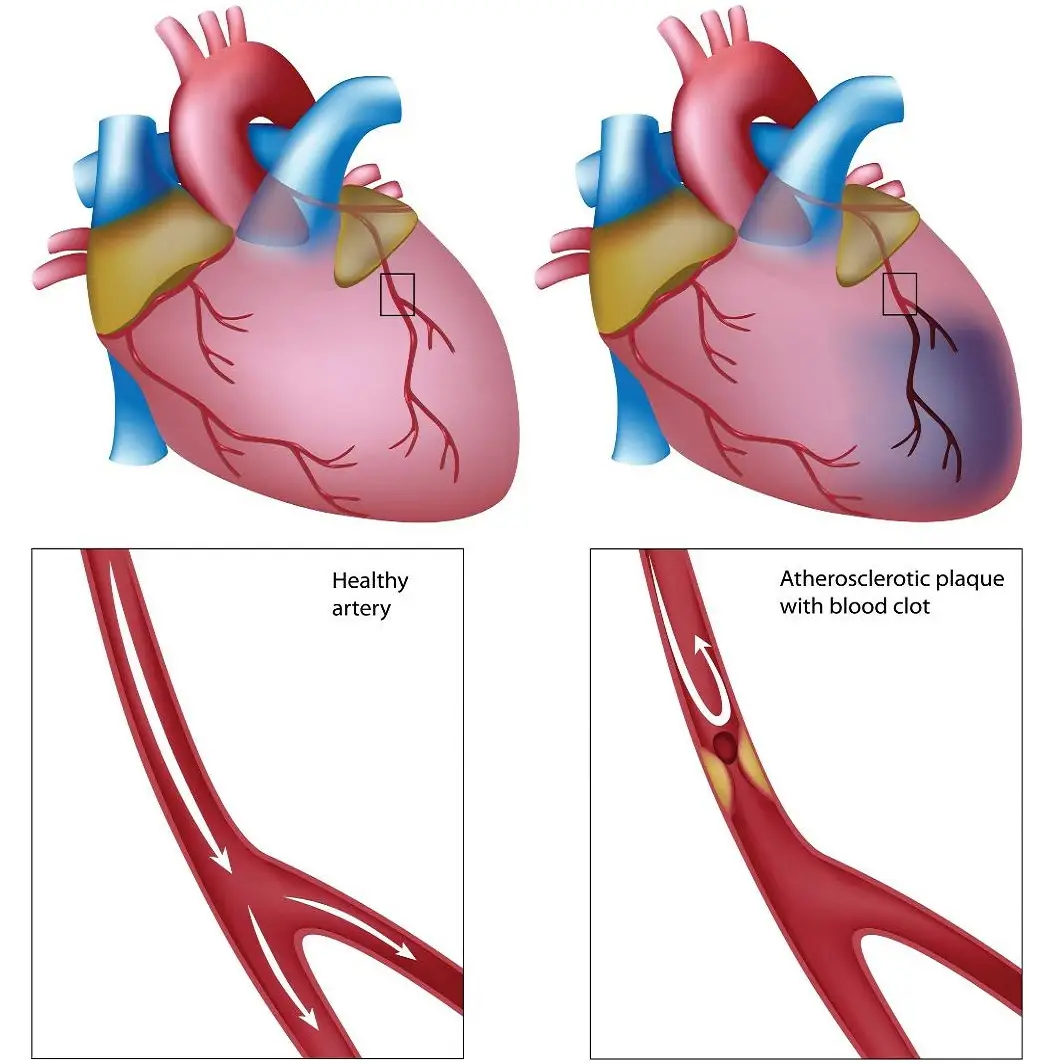
Myocardial infarction (MI) occurs when a blockage or narrowing of the coronary artery reduces or prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart muscle. This can happen due to plaque buildup of fatty deposits and other substances. As the artery narrows, less blood can pass through, leading to decreased oxygen supply and, eventually, tissue death in the affected area.
If left untreated, MI can cause major damage to the heart, leading to life-threatening complications such as cardiac arrest or stroke. Immediate medical treatment is required to prevent serious damage or death.
Symptoms
Myocardial infarction (MI) symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, depending on the individual. The most common symptoms of MI include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and sweating.
These symptoms can be debilitating and may affect daily activities such as climbing stairs, physical activity, or work duties.
It is important to seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms are present, as prompt treatment is essential for preventing more serious damage. In addition to seeking medical help when experiencing MI symptoms, patients should also take steps to reduce their risk factors, such as exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet.
Causes
A blockage causes myocardial infarction (MI) in the coronary arteries, which provide oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. The blockage is usually due to atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque consisting of fatty deposits and other substances on the inner walls of the artery. This can eventually lead to the narrowing of the artery and oxygen deprivation of the heart muscle cells.
Other lifestyle factors such as smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity can increase an individual's risk for MI. It is important to reduce these risk factors through regular exercise, healthy eating, not smoking, and, if needed, taking medication prescribed by a doctor.
Diagnosis
Myocardial infarction (MI) is typically diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG) test. This test involves attaching electrodes to the chest, arms, and legs to measure electrical signals traveling through the heart. The ECG can detect any changes in the heart's rhythm, which could indicate a heart attack.
Furthermore, other tests, such as blood tests or echocardiograms, may be combined with an ECG to reach an accurate diagnosis. Getting a correct diagnosis is essential for treatment decisions, as it helps guide physicians on how to best proceed with treatment plans.
Treatment
Myocardial infarction (MI) can be treated with medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle changes. Medications such as aspirin or anticoagulants may be used to keep the blood from clotting and reduce heart inflammation.
Surgery may involve inserting a stent in the blocked artery to open it up again for improved blood flow. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating healthy, exercising regularly, and managing stress can also help reduce an individual's risk of experiencing an MI in the future.
There are many stories of successful outcomes from patients who have undergone MI treatment, showing that timely intervention and proper care can significantly improve symptoms and reduce the risk of further complications.
Recovery
For those who have experienced a myocardial infarction (MI), recovery is an important part of restoring the heart's health. Follow-up care with a medical professional is highly encouraged, as it can help maintain cardiac health and reduce the risk of further complications.
Cardiac rehabilitation is also recommended for individuals who have suffered from an MI, as it helps strengthen their heart muscles and improve circulation. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as eating healthy, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can drastically improve one's outlook after experiencing an MI.
Lastly, managing anxiety and depression that can often accompany a heart attack is essential for recovering physically and mentally from this experience.
Prevention
Taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle is an important part of preventing myocardial infarction (MI) from developing or recurring. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet low in saturated fat and rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, managing stress levels, and controlling risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol.
It is recommended to limit alcohol consumption and avoid the use of smoking or recreational drugs. Consistent check-ups with a doctor can help monitor vital signs and alert an individual to any changes that could increase the risk of MI. Taking proactive steps toward prevention can be invaluable in providing long-term health benefits for patients.
Conclusion
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a serious cardiovascular event that can impact an individual's health if not treated properly. It is important for those who have experienced an MI to receive proper follow-up care and engage in cardiac rehabilitation to restore their health and reduce the risk of further complications.
Additionally, lifestyle changes such as eating healthy, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, managing stress levels, and controlling risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol are all key steps to prevent MI from developing or recurring. If you are experiencing any symptoms of MI, it is advised that you seek medical attention immediately.
To ensure the best possible care for your heart condition, we encourage patients to visit our clinic for specialized treatments and personalized plans tailored to each patient's needs.


