Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) are two types of implantable devices that can be used to treat certain conditions related to the heart. While ICDs and CRT have been proven to improve cardiac function, understanding the potential risks and benefits associated with their use is important for improving patient outcomes. Let's discuss what ICDs and CRT are, how they work, who can benefit from their use, and why patients need to understand these procedures.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs)
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) are surgically implanted in the chest to
detect and treat abnormal heart rhythms. They consist of two parts: a monitor, which is installed beneath the skin, and a generator, which delivers charge when necessary.The monitor monitors the heart rhythm, looking for abnormal activity that might indicate arrhythmia. If it detects such activity, it will send a signal to the generator, delivering a shock to restore normal heart rhythms. ICDs are used to treat conditions such as ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia.
Benefits of ICDs
ICDs (Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators) are highly effective for preventing sudden cardiac arrest (SCA). When implanted in the body, they can detect and automatically respond to dangerous changes in heart rate. In the event of SCA, an ICD will send an electrical shock to the heart to restore it to a normal rhythm. This can be life-saving and is especially beneficial for people with existing heart conditions who may be at a higher risk of developing SCA.
In addition to providing a safety net against SCA, ICDs also help monitor patients' heart rates. They provide detailed information about the patient's condition that doctors can use to make informed treatment decisions. Due to their high effectiveness, ICDs have become increasingly popular among those at risk of developing SCA or other cardiac disease types.
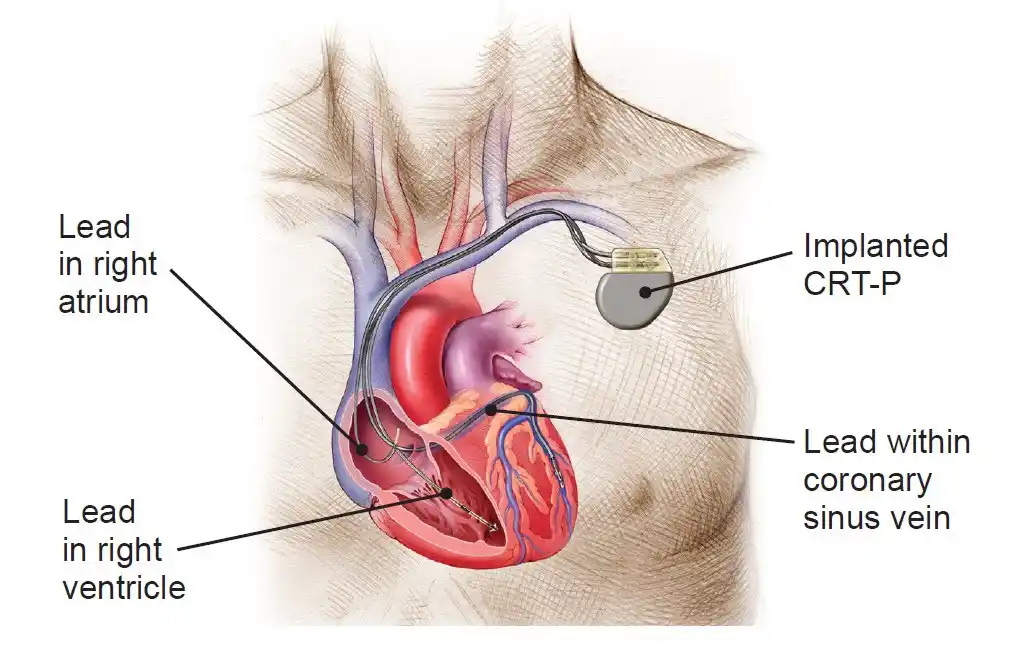
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a medical device surgically implanted in the chest to help improve heart function. It consists of two parts: an electrode on each ventricle and a generator containing a battery and electronics.
The electrodes send electrical signals to the heart through the generator, which helps synchronize the contractions of both ventricles for improved pumping ability. CRT treats conditions such as congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation and can help improve the quality of life for those suffering from heart disease.
Benefits of CRTs
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) is a form of implantation therapy used to improve heart function and reduce symptoms associated with heart failure. It utilizes an electrical device called a biventricular pacemaker, which consists of three lead wires connected to the ventricles. This technology can sense the heart's electrical activity, then send small pulses to coordinate the contraction of both ventricles.
The benefits of CRT are multi-faceted. In addition to increasing overall heart function, it can reduce symptoms such as fatigue and shortness of breath due to decreased cardiac output. It has also effectively decreased hospital admissions and mortality rates among patients with severe forms of heart failure. Furthermore, studies have found that CRT implantation is associated with improved exercise capacity and quality of life in individuals with this condition.
Conditions Treated with ICD and CRT Implantation
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) implantation can be used to treat various conditions that affect the heart. ICDs are primarily used to treat ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia, while CRT is often used to treat congestive heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
By implanting these devices, patients can find relief from the symptoms of their condition(s) and improve the quality of life. ICDs provide an extra safety net by constantly monitoring the heart's rhythm for signs of irregular activity. If this activity is detected, a shock will be delivered to restore normal rhythm. CRT helps synchronize the contractions of both ventricles, thereby increasing efficiency and helping reduce fatigue due to overworking one side. This can also help improve blood flow, providing an essential nutrient-rich supply throughout the body.
Overall, both devices offer tremendous benefits to those suffering from heart disease, helping them live longer and healthier lives.
Preparation
Preparing for an ICD or CRT implantation procedure is an important step in the overall success of the treatment. Before the procedure, patients should discuss any medications they are taking with their physician and avoid taking non-essential drugs or supplements 48 hours before the operation. Patients should not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before the procedure.
During the procedure, patients can expect to be sedated to minimize discomfort. The time required for the surgery will depend on the type of device being implanted and other individual factors; usually, it takes between 30 minutes and two hours. After surgery, most patients can expect to stay overnight in the hospital but may be able to return home on the same day if their recovery is progressing well.
Procedure
The ICD/CRT implantation procedure begins with administering a local anesthetic to reduce pain or discomfort. Once the patient is sedated, a small incision is made to access the chest area. The device is placed just under the skin, and wires are connected to it that lead directly to the heart. After it has been secured, electrical tests will be carried out to ensure everything functions correctly.
Once all testing has been completed, the incision site is closed and bandaged. If a CRT device were being implanted, then additional leads would be attached at this time. Finally, once all procedures have been completed successfully, patients can expect to be monitored in recovery for 1-2 hours before they are discharged from the hospital. Throughout the process, patients should experience minimal pain or discomfort due to using anesthetics and other pain management techniques.
Recovery
Following the ICD/CRT implantation procedure, patients can expect to stay overnight for monitoring. During recovery, medical staff will closely monitor them to ensure that there are no major complications and that their condition is stable. Once cleared by a cardiologist, most patients can expect to return home either immediately or within 24 hours.
Patients should follow their doctor's instructions at home concerning medications, physical activity, and dietary restrictions. They should also avoid strenuous activities during the first few weeks following the procedure and watch for any signs of infection or bleeding. With proper care and attention, most people fully recover from this type of surgery without major difficulties.
Final Advice
Conversation with your cardiologist before considering any of these treatments is key, as they have the expertise and experience necessary to understand your unique circumstances and advise on the best course of action. Don't hesitate to reach out - chances are they'll be more than happy to answer any questions you may have!


