Coronary Artery Disease
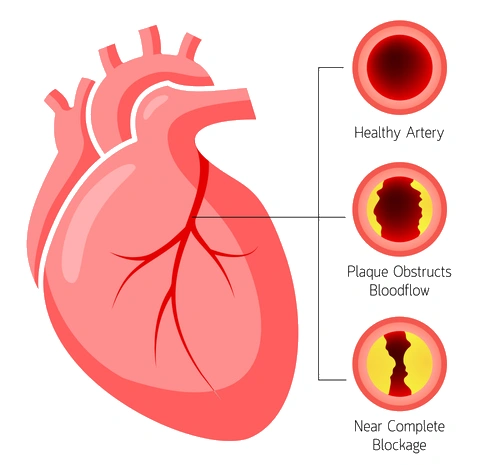
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is caused by the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries that supply blood to the heart. This can lead to a blockage in these arteries, restricting or completely cutting off oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart muscle. If untreated, CAD can cause chest pain, heart attack, arrhythmias, and even sudden death.
In India, the prevalence of CAD has steadily increased in recent years. According to research published in 2020, an estimated 27 million people are living with this condition in India, and it is estimated that there will be 37 million cases by 2030. Additionally, coronary artery disease is responsible for up to 20 per cent of deaths among adults aged 30–69 in India.
Given its prevalence and potential consequences, patients must understand what CAD is and how it impacts their health.
Symptoms
Coronary artery disease can cause various symptoms, including chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, and lightheadedness. These symptoms may come and go or may be present all the time. Occasionally, CAD can lead to heart attack and sudden death if left untreated.
These symptoms can have a significant impact on daily life. For example, chest pain or shortness of breath while doing simple activities like walking up stairs might indicate CAD. Additionally, fatigue or exhaustion without physical exertion could indicate the condition.
If you experience these symptoms, please speak with your doctor immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in helping to reduce the risk of more serious complications related to coronary artery disease.
Causes & risk factors
Coronary artery disease occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become blocked or narrowed. This can happen due to fatty deposits in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. These deposits comprise cholesterol, calcium, and other substances in the blood.
Several lifestyle factors can contribute to plaque formation and CAD development, including smoking, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Additionally, age plays an important role in CAD. The risk of developing CAD increases with age as our arteries become more prone to plaque buildup over time. Family history is also a risk factor for coronary artery disease - having family members with CAD will increase your risk of developing this condition.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing coronary artery disease usually begins with a physical examination, a review of symptoms, and medical history. Depending on the results, your physician may order laboratory tests such as blood work or an electrocardiogram (ECG).
Further imaging tests may sometimes be necessary to confirm or rule out a diagnosis. Common imaging tests for CAD include echocardiography (heart ultrasound) and computed tomography (CT) scans. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be used.
It is important to get an accurate diagnosis of coronary artery disease so that your healthcare provider can make the best possible treatment decisions. Early diagnosis and treatment can help reduce the risk of more serious complications related to this condition.
Treatment
Several treatment options are available for coronary artery disease, including medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures.
Medications help prevent further blockages in the arteries and reduce symptoms of the condition. Common medications used for CAD include antiplatelet agents such as aspirin; lipid-lowering drugs like statins; anticoagulants such as warfarin; and blood pressure medications.
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes can be beneficial in treating and managing coronary artery disease. Lifestyle modifications can include quitting smoking, improving diet, increasing physical activity, and reducing stress. Surgical procedures may be recommended for patients with more severe blockages or those who do not respond well to other treatments.
Types of surgery typically used for CAD treatment include angioplasty (to widen the blocked artery), stent placement (to keep the artery open), bypass surgery (to reroute blood around a blockage), and cardiac ablation (to destroy the tissue causing abnormal heart rhythms).
Successful outcomes from these treatments depend on factors such as the severity of the condition, how early it was diagnosed, adherence to treatment recommendations, and individual response to medications/procedures.
Prevention
Preventing coronary artery disease or reducing the risk of its recurrence or progression is possible by making a few lifestyle changes.
Avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce your risk, as smoking increases plaque buildup in the arteries. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is also important, as obesity increases the chance of developing CAD. Regular physical activity and increasing intake of fibre-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce cholesterol levels.
Another key way to prevent CAD is limiting alcohol consumption, as excessive drinking can further damage your heart health. Lastly, getting regular check-ups with a cardiologist is important so that any potential risk factors or signs of CAD can be detected and treated early on.
Conclusion
The various treatments and preventive measures for coronary artery disease can help improve the quality of life for patients with this condition. Medications, lifestyle changes, and surgical procedures can all effectively treat CAD. However, patients must take proactive steps to prevent the condition from developing or progressing, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular check-ups with a cardiologist.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of coronary artery disease, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, seek medical attention immediately. It is important to visit our heart clinic for early detection and treatment of CAD to avoid potential complications.


