Dual Chamber Pacemakers for innovative Cardiac Treatment
Dealing with irregular heartbeats can be challenging, but there's a solution that can make a significant difference. The Dual Chamber Pacemaker is a remarkable device designed to restore the natural rhythm of your heartbeat.
In this blog post, We’ll explain what a Dual Chamber Pacemaker is, how it works, and how it can benefit patients with some specific conditions. Now let's dive into what exactly is a dual chamber pacemaker and why you should consider it as an option if you’re living with certain Heart conditions.

If you're searching for an experienced specialist to perform the implantation, Dr. Abhijeet Palshikar at Cardiomet Clinic, Pacemaker Implantation in Pune is the right choice. With his expertise and dedication to patient care, he will ensure that you Receive the best possible treatment and support for your heart condition
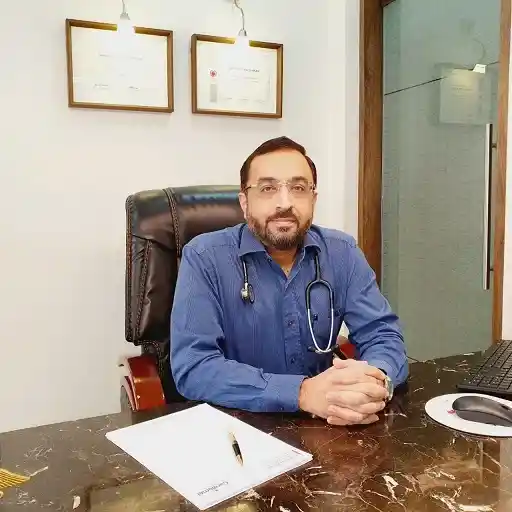

where is Pacemaker Dual-Chamber implanted?
A Dual-chamber Pacemaker is a small, battery-operated medical device implanted under the skin near the collarbone to help regulate abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
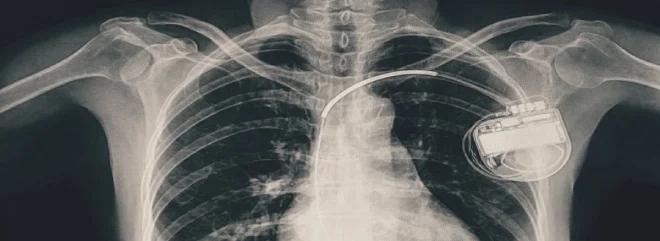
It Consists of two essential components: the pulse generator, which contains the battery and electronic circuitry, and the leads, which are thin, insulated wires that connect the pulse generator to specific chambers of the heart.
As the name suggests, a Dual-Chamber Pacemaker has two leads one connected to the right atrium and the other to the right ventricle allowing it to monitor and stimulate both chambers as needed.
How does a dual-chamber Pacemaker work?
A Dual Chamber Pacemaker Constantly monitors the electrical activity of the heart. It generates electrical impulses to Correct the issue when it detects an abnormal rhythm, such as a heart rate that's too slow (bradycardia) or a delay in the electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles (heart block).
These impulses travel through the leads to the heart, stimulating the atria and ventricles to contract in a coordinated manner, thereby restoring a normal heartbeat.
By synchronizing the contractions of the atria and ventricles, a dual chamber pacemaker ensures efficient blood flow throughout the body and can help alleviate symptoms associated with Arrhythmias, such as fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Who needs a Dual-Chamber Pacemaker?
A Dual Chamber Pacemaker may be recommended for patients with specific types of heart rhythm disorders, including:
- Sick sinus syndrome: A condition in which the heart's natural pacemaker (sinoatrial node) fails to generate adequate electrical signals, leading to a slow or irregular heartbeat.
- Atrioventricular (AV) block: A disruption in the electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles, which can result in a slow, irregular, or uncoordinated heartbeat.
- Bradycardia-tachycardia syndrome: A condition characterized by alternating episodes of abnormally slow and fast heart rates, often seen in patients with atrial fibrillation.
The decision to implant a dual chamber pacemaker is based on a thorough evaluation of the patient's specific needs, symptoms, overall health, and the potential benefits and risks associated with the device.
Types of Dual-Chamber Pacemakers and how to Choose the Correct One?
Although dual chamber pacemakers share the common feature of having two leads one for the right atrium and one for the right ventricle there are variations in terms of additional features, programming Capabilities, and Manufacturer specific technologies. Here are some factors to consider when choosing the most suitable dual chamber pacemaker for a patient:
- Rate-responsive pacing: Some dual chamber pacemakers offer rate-responsive pacing, which allows the device to adjust the heart rate based on the patient's activity level and physiological needs. This feature is particularly beneficial for patients who require a more dynamic heart rate response during exercise or other physical activities.
- Adaptive algorithms: Advanced pacemakers may incorporate adaptive algorithms that can optimize atrioventricular (AV) delay, minimize unnecessary right ventricular pacing, or detect and treat atrial arrhythmias. These features can help improve cardiac function and reduce the risk of complications, such as heart failure or atrial fibrillation.
- MRI compatibility: Not all pacemakers are compatible with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. If a patient is likely to require MRI scans in the future, it's essential to choose a pacemaker that is specifically designed to be MRI-safe.
- Battery life: The battery life of a pacemaker is an important consideration, as it determines how often the device will need to be replaced. Longer battery life can reduce the frequency of replacement surgeries and associated risks.
- Manufacturer and model: Different manufacturers offer various models of dual chamber pacemakers, each with its own set of features and capabilities. It's essential to compare the available options and select the one that best meets the patient's specific needs and preferences.


Ultimately, the choice of a dual chamber pacemaker should be based on a comprehensive assessment of the patient's medical history, lifestyle, and unique requirements.
A Cardiologist or Electrophysiologist will work closely with the patient to determine the most appropriate device, taking into account factors such as the type and severity of the Arrhythmia, patient's age, activity level, and any potential contraindications or risks associated with the implantation procedure.
Benefits
Dual chamber pacemakers offer a number of benefits for patients with specific heart rhythm disorders, helping to improve overall Cardiac Function and enhance their quality of life.
Some key benefits include:
- Improved heart Rate control: By monitoring and stimulating both the right atrium and the Right Ventricle, Dual Chamber Pacemakers can provide more precise control over the Heart's Rhythm. This ensures that the atria and ventricles contract in a coordinated manner, resulting in a more consistent and efficient heartbeat.
- Reduced Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation is a common type of arrhythmia characterized by rapid and irregular contractions of the atria.
- Improved Quality of life: By effectively regulating the heart's rhythm and ensuring proper blood flow throughout the body, dual chamber pacemakers can help alleviate symptoms associated with arrhythmias, such as fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
Studies have shown that dual chamber pacing can reduce the risk of developing atrial fibrillation compared to single-chamber pacemakers, particularly in patients with sinus node dysfunction or atrioventricular block.

As a result, patients may experience an improved quality of life, with increased energy levels, better exercise tolerance, and reduced limitations on daily activities.
Dual Chamber Pacemakers offer an important treatment solution for individuals with specific heart rhythm disorders, effectively restoring normal Cardiac function and improving overall well-being. If you are seeking Pacemaker Treatment in Pune, Dr. Abhijeet Palshikar can provide expert care and guidance.
Risks involved
While dual chamber pacemakers are generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications associated with their implantation and use. Some of these include:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the incision site or around the pacemaker itself. Proper care of the wound and adherence to post-operative instructions can help minimize this risk.
- Bleeding: Bleeding may occur during or after the implantation procedure, particularly in patients with Clotting Disorders or those taking Blood-thinning medications. Careful monitoring and appropriate adjustments to medications can help reduce the risk of bleeding complications.
- Lead problems: The leads connecting the pacemaker to the heart may become dislodged, fractured, or damaged over time. This can affect the device's ability to deliver pacing pulses effectively. In some cases, lead-related issues may require a minor surgical procedure to reposition or replace the affected lead.
- Pacemaker syndrome: Pacemaker syndrome is a rare complication that occurs when the atria and ventricles contract out of sync, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, and fatigue.This issue can often be resolved by adjusting the pacemaker's settings or, in some cases, upgrading to a biventricular pacemaker.
- Oversensing: Oversensing occurs when the pacemaker detects electrical signals that are not actual heartbeats, such as muscle contractions or external interference. This can cause the device to inappropriately withhold pacing pulses, potentially leading to a slow heart rate or other arrhythmias. Adjusting the pacemaker's settings can usually correct oversensing issues.
- Undersensing: Undersensing is the opposite of oversensing it occurs when the pacemaker fails to detect the heart's natural electrical signals. This can result in unnecessary pacing pulses or a failure to pace when needed. As with oversensing, adjustments to the device's settings can often resolve undersensing issues.
It's important for patients with pacemakers to attend regular follow-up appointments and promptly report any unusual symptoms or concerns to their cardiologist. This proactive approach will help ensure that any issues are detected and addressed promptly, maximizing the benefits of the pacemaker and preserving the patient's cardiac health.
The pacemaker implantation procedure
The implantation of a Pacemaker is a relatively straightforward surgical procedure, typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation. Here are the main steps involved:
- The patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the area where the pacemaker will be implanted, usually on the left side of the chest, just below the collarbone.
- A small incision is made, and the pacemaker leads are guided through a vein into the heart using Fluoroscopic (X-ray) Guidance.
- Once the leads are in place, they are tested to ensure proper functioning and positioning. Any necessary adjustments are made at this stage.
- The Pulse Generator, which houses the battery and electronic circuitry, is connected to the leads and inserted into a pocket created under the skin.
- The incision is closed using sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to protect the wound.
The entire procedure usually takes 1-2 hours, and most patients can return home within 24 hours. Some discomfort, swelling, or bruising may be experienced after the surgery, but these symptoms generally subside within a few days to a week.
Pacemaker programming
After the pacemaker is implanted, it must be programmed to suit the patient's specific needs. A cardiologist or electrophysiologist will use an external programmer—a specialized computer that communicates with the pacemaker via wireless signals—to adjust the device's settings, such as pacing rate, pacing mode, and sensitivity to the heart's electrical signals.
Pacemaker programming is non-invasive and painless, and adjustments can be made during follow-up visits to optimize the device's performance and ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
Pacemaker troubleshooting
In rare cases, a pacemaker may malfunction or require adjustments to function optimally. Some common issues that may require troubleshooting include:
- Lead dislodgement: If a lead becomes dislodged from its intended position, the pacemaker may not be able to provide effective pacing. This issue can be detected during routine follow-ups or if the patient experiences symptoms such as dizziness, shortness of breath, or palpitations. The lead may need to be repositioned through a minor surgical procedure.
- Battery depletion: Over time, the pacemaker's battery will deplete, and the device will need to be replaced. Regular follow-ups will help monitor battery life and schedule a replacement before the battery is fully exhausted.
- Inappropriate Pacing: If the patient experiences symptoms that indicate the pacemaker is not functioning optimally, the device's settings may need to be adjusted via external programming.
It's important for patients with pacemakers to attend regular follow-up appointments and promptly report any unusual symptoms or concerns to their cardiologist. This proactive approach will help ensure that any issues are detected and addressed promptly, maximizing the benefits of the pacemaker and preserving the patient's cardiac health.
What is the cost of a Biventricular Pacemaker in Pune?
The cost of a biventricular pacemaker, also known as a cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) device, can vary depending on the hospital, the specific device model, and other factors such as physician fees and insurance coverage. In Pune, India, the cost of a biventricular pacemaker implantation procedure may range from approximately 2 to 5 lakh Indian Rupees (INR) or more.
It's essential to Consult with a cardiologist or electrophysiologist in Pune to get an accurate cost estimate based on your specific needs and circumstances. Additionally, it's important to consider whether your insurance plan covers the cost of the device and the implantation procedure, as this can significantly impact out-of-pocket expenses.
Commonly asked questions
- What is the purpose of a dual chamber pacemaker?
- What is the difference Between single and double chamber pacemaker?
- How long can you live with a dual pacemaker?
- Can a pacemaker also be a defibrillator?
The purpose of a dual chamber pacemaker is to help regulate Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) by monitoring and stimulating both the right atrium and the right ventricle of the heart.
By synchronizing the contractions of these chambers, a Dual Chamber Pacemaker ensures efficient blood flow throughout the body and can alleviate symptoms associated with arrhythmias, such as fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.
A single chamber pacemaker has one lead that connects the pulse generator to either the right atrium or the right ventricle, while a dual-chamber (double chamber) pacemaker has two leads—one connected to the right atrium and the other to the right ventricle. This allows a dual chamber pacemaker to monitor and stimulate both chambers, providing more precise control over the heart's rhythm and improving overall cardiac function.
There is no specific lifespan for individuals with a dual chamber pacemaker. Many patients can live normal, healthy lives for several years or even decades after receiving a pacemaker, depending on their overall health, age, and underlying heart condition. The pacemaker device itself typically has a battery life of 5 to 15 years, after which it will need to be replaced through a minor surgical procedure.
Yes, a device called an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) combines the functions of a pacemaker and a defibrillator. An ICD constantly monitors the heart's rhythm and can deliver low-energy pacing pulses to correct minor arrhythmias or high-energy shocks to terminate life-threatening arrhythmias, such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
These devices are typically recommended for patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death due to severe ventricular arrhythmias.
In conclusion, dual chamber pacemakers are valuable treatment options for patients with specific heart rhythm disorders, offering benefits such as improved heart rate control, reduced risk of atrial fibrillation, and enhanced quality of life. However, it's essential to be aware of potential risks and complications, including infection, bleeding, lead problems, Pacemaker syndrome, oversensing, and undersensing.
If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms of an arrhythmia or has been diagnosed with a heart rhythm disorder, consult with a cardiologist or electrophysiologist to determine if a Dual-Chamber Pacemaker is the most appropriate treatment option.
Remember that regular follow-up appointments and open communication with your cardiologist are crucial for ensuring the best possible outcome and maintaining your cardiac health.
Don't let heart Rhythm disorders hold you back take action today and explore the potential benefits of a dual chamber pacemaker for improved cardiac function and a better quality of life.




